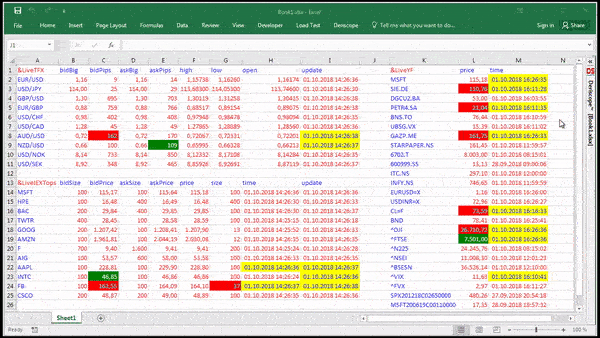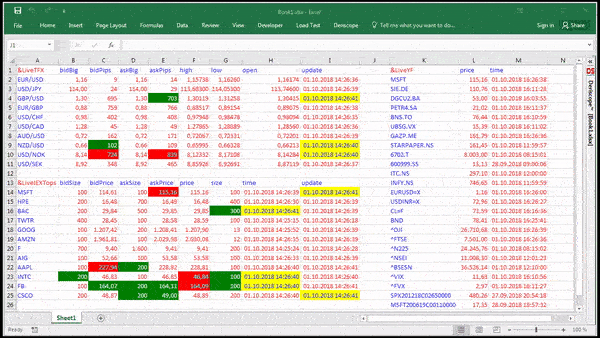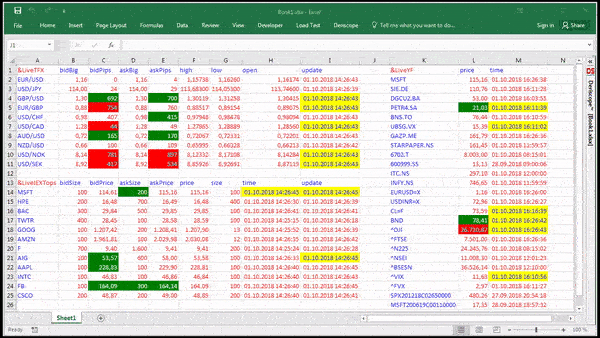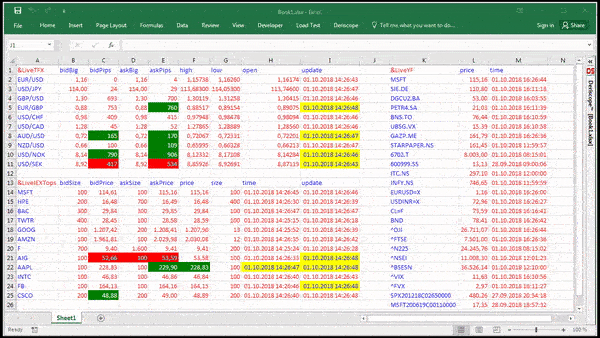
I use the RTD function in Excel and the cell that is being imported from the Stock Broker website (Think or Swim; TD Ameritrade) is bringing in a cell that shows an expected move of a stock. The Execl spreadsheet cell is importing a '+/-' signs in front of a number which is imported using the RTD function. Excel For Mac Rtd Functions Think Or Swim Peatix. Excel Details: Excel For Mac Rtd Functions Think Or Swim Tutorial. A couple small adjustments improve the look of the chart. First, the vertical axis scale of 0 to 11 leaves rather wide margins above and below the data. Because RTD is a function in Excel, you can take full advantage of the power of Excel with functionality such as cell referencing. To see all of the functions supported in exported data, click on the “Data Export Help” option on the Printer menu. 1) I think I will use daily data eventually, but at the outset I just used your original strategy. So I will apply the fix later. First I need to learn where to put the code, this is my first time using Think Script, so give me a day or two. I found this forum because I googled 'is there any way to download OHLC from ThinkOrSwim'.
- Excel Rtd Functions Think Or Swim Using
- Excel Rtd Functions Think Or Swim Free
- Excel Rtd Thinkorswim
- Excel Rtd Function
Note
Office 365 ProPlus is being renamed to Microsoft 365 Apps for enterprise. For more information about this change, read this blog post.
Summary
Note
The performance of the RealTimeData (RTD) function has been greatly enhanced in Excel M365 version 2002 or later. For more information, see Excel Performance and Limits Improvements.
This article describes the functionality that the RealTimeData (RTD) function provides. Microsoft Office Excel provides a worksheet function, RealTimeData (RTD). This function enables you to call a Component Object Model (COM) Automation server to retrieve data in real time.
When you have to create a workbook that includes data that is updated in real time, for example, financial data or scientific data, you can now use the RTD worksheet function. In earlier versions of Excel, Dynamic Data Exchange (DDE) is used for that purpose. The RTD function is based on COM technology and provides advantages in robustness, reliability, and convenience. RTD depends on the availability of an RTD server to make the real-time data available to Excel. For more information about how to create an RTD server, see the 'References' section.
The RTD function retrieves data from an RTD server for use in the workbook. The function result is updated whenever new data becomes available from the server and the workbook can accept it. The server waits until Excel is idle before updating. This relieves the developer of having to determine whether Excel is available to accept updates. The RTD function differs from other functions in this regard because other functions are updated only when the worksheet is recalculated.
Although the RTD function provides a link to data on a server, it is not the same type of link as references to cells in other worksheets or workbooks. For example, if you use the RTD function in a workbook, you do not receive the Links startup message when you open the workbook, nor can you manage the status of an RTD function through the Edit Links dialog box.
Syntax
The RTD function uses the following syntax
=RTD(RealTimeServerProgID,ServerName,Topic1,[Topic2], ...)

where the function arguments are as follows:
RealTimeServerProgID
A string that represents the Program ID of the RTD server installed on the local system. This is typically a COM add-in that is registered by a setup procedure or by using RegSvr32. RealTimeServerProgID is a required argument.
ServerName
A string that represents the name of the server on which the RTD server is to be run. If the RTD server is run locally, the ServerName should be an empty string (') or omitted.
Topic1, [Topic2], ...
Strings that determine the data being retrieved. You can use from one to 28 topics, although only one topic is required.
Using RTD
As an example of the RTD function, consider retrieving information from a server that delivers continuous data for runners in several simultaneous races. Assume that the server is provided as a Dynamic Link Library (DLL) named RaceReport.dll, that it is installed on the user's computer, and that it is registered as a COM add-in by its own setup process. The general form of the RTD function as used with this server might be as follows
=RTD('MyRTDServerProdID','MyServer','RaceNum','RunnerID','StatType')
where the topics RaceNum, RunnerID, and StatType determine the race of interest, the runner whose data is required, and the type of data for a particular use of the function, respectively.
Here the user might select a cell and type the following formula in it
Excel Rtd Functions Think Or Swim Using
=RTD('ExcelRTD.RaceReport',','2','16','Time')
to see the current elapsed time for runner number 16 in race number 2. The number of topics and the nature of the associated data is determined by the developer of the COM server. For example, the race-reporting server might deliver different data if you use the following RTD function:
=RTD('ExcelRTD.RaceReport',','3','25','Position')
In this case, the data returned indicates the current position of runner number 25 in race number 3.
In this manner, the same function can be used differently throughout the workbook to retrieve different data from the same server, all of which is updated automatically.
Wrappers to Simplify Use
The RTD function can be used inside user-defined functions (UDFs) in Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications. These then become wrappers for the RTD function. This approach can be useful in shielding users from the details of the RTD server name and ProgID, and in enabling them to focus only on the data that is important to them.
Excel Rtd Functions Think Or Swim Free
For example, in the previous scenario, the user might be provided with two functions: GetTime(RunnerID) and GetPosition(RunnerID). These functions assume that the user is always dealing with the same server and race number. Therefore the user only has to specify a runner's ID to receive current data on the runner's elapsed time and position, respectively.
Calculation
Because RTD updates data when Excel is idle, it continues to receive information if Excel is in manual calculation mode. In that event, the new data is cached and the current values are used when a manual calculation is performed.
Security
RTD servers should be digitally signed. If an RTD server is not digitally signed, the server may not load, and a #N/A will be displayed in the cell(s) referencing the RTD server.
For Microsoft Office Excel 2007, you can review security settings by using the Trust Center. This can be accessed by from the Trust Center tab in the Excel Options dialog box.
For Microsoft Office Excel 2003 and in Microsoft Excel 2002, the load behavior can be altered by adjusting the macro security settings in Excel.
Excel Rtd Thinkorswim
References
For more information about RTD and Excel security, see How to set up and use the RTD function in Excel.
For more information about creating an RTD server, see How to create a RealTimeData server for Excel.
Ubuntu's Apache2 default configuration is different from the upstream default configuration, and split into several files optimized for interaction with Ubuntu tools. The configuration system is fully documented in /usr/share/doc/apache2/README.Debian.gz. Refer to this for the full documentation. Documentation for the web server itself can be found by accessing the manual if the apache2-doc package was installed on this server.
Excel Rtd Function
The configuration layout for an Apache2 web server installation on Ubuntu systems is as follows:
- apache2.conf is the main configuration file. It puts the pieces together by including all remaining configuration files when starting up the web server.
- ports.conf is always included from the main configuration file. It is used to determine the listening ports for incoming connections, and this file can be customized anytime.
- Configuration files in the mods-enabled/, conf-enabled/ and sites-enabled/ directories contain particular configuration snippets which manage modules, global configuration fragments, or virtual host configurations, respectively.
- They are activated by symlinking available configuration files from their respective *-available/ counterparts. These should be managed by using our helpers a2enmod, a2dismod, a2ensite, a2dissite, and a2enconf, a2disconf . See their respective man pages for detailed information.
- The binary is called apache2. Due to the use of environment variables, in the default configuration, apache2 needs to be started/stopped with /etc/init.d/apache2 or apache2ctl. Calling /usr/bin/apache2 directly will not work with the default configuration.